ECMAScript Expressions
Contents
In certain blocks, you can use ECMAScript expressions to perform dynamic operations while an application is running. For example, you can use ECMAScript expressions to assign values to variables or perform certain functions, like sorting an array.
Before you start
To use this feature, you must have a basic level of familiarity and understanding of ECMAScript syntax and rules.
Although the terms ECMAScript and JavaScript are often used interchangeably, Designer technically supports ECMAScript and does not support JavaScript functions that are typically used for web-browser based applications, such as pop-up windows, alerts, and so on.
Designer blocks that support the use of ECMAScript expressions include:
- Assign Variables Block
- Menu Option Block
- Return Block
- Shared Module Block
- Data Tables
- Activity Block
- Milestone Block
A few notes on syntax
Some rules and guidelines to follow when using ECMAScript in Designer:
- Strings must be quoted (
'). For example,'hello'is a string, whereashellois a reference to a variable called hello. - Single quotes (
') are recommended, as opposed to double quotes ("). - When specifying an object in JSON notation, surround the JSON with parentheses. For example:
({'abc': 'def'}).
Use caution! Any errors in your script can cause erratic behavior, so test your changes to make sure that your script works correctly before running it in your production environment. Designer can check your script for syntax errors, but cannot validate it nor check for runtime errors that might occur when the script is executed.
Examples of how ECMAScript can be used
Below are examples of how ECMAScript expressions can be used in Designer applications.
Building a Dynamic TTS Prompt
You can use the Assign block to concatenate a string to be spoken by the application. For example, the expression below reads the caller's phone number or ID:
'You are calling from ' + ANI
Controlling the Application Flow
A Segmentation block can take ECMAScript expressions that evaluate to a Boolean value, and thus control the flow of the application.
For example, you might want to inform your customers about upcoming seasonal events and you need a way to determine the current season and whether the event is occurring within the coming week. The expression below determines whether the call was received within seven days of the event, and whether the current season is summer or autumn:
numDays > 7 && (isSummer | | isAutumn)
Advanced scripting in Designer
In blocks where it is supported, you can use use the Advanced Scripting tab to compose more complex ECMAScript constructs, such as loops or multiple nested conditions.
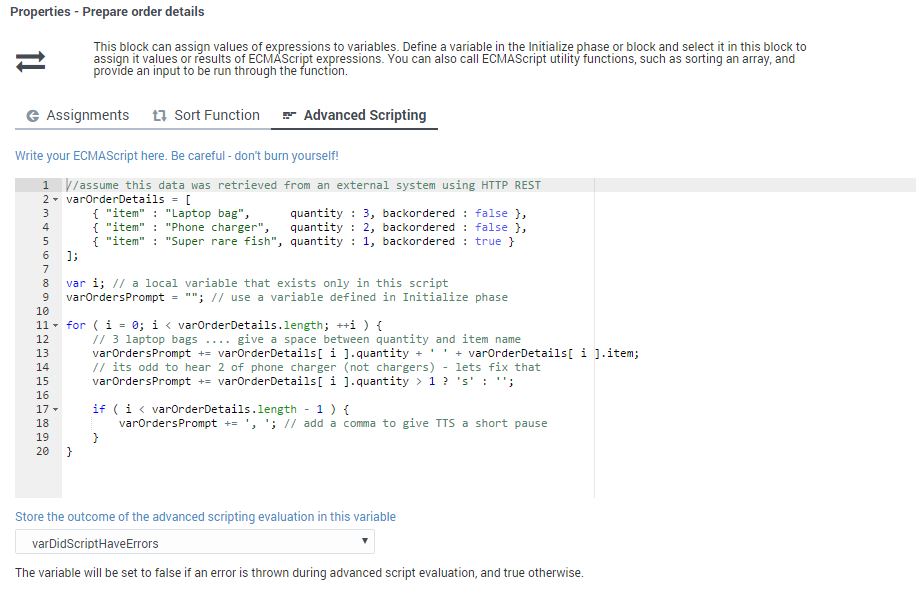
Let's take a look at how advanced scripting could be used to assign a value to a variable. Here, some script has been added to the Advanced Scripting tab of an Assign Variables Block:
In this example, the script sets the variable varOrdersPrompt to 3 Laptop bags, 2 Phone chargers, 1 Super rare fish.
Here's how it works:
The sample script first initializes JSON data in varOrderDetails so that it becomes an array of three JSON objects. Each JSON object has properties — item, quantity, and backordered. The script then proceeds to loop through orders and forms a string to play back to the caller to notify them of their order status.
The script uses variables in two scopes:
- A scope exclusive or local to this script itself (
i). This variable remains available only while this script runs, and then it disappears. - Top-level variables that were defined in the Initialize phase remain available throughout this application flow, but not in any modules this application calls (such as
varOrdersPrompt).
Built-in user functions
Designer also has built-in ECMAScripts that you can invoke from a Designer application, such as from an Assign or Segmentation block, to perform certain functions at runtime.
setAttributes
You can use this function to add arbitrary key/value pairs to the Session Detail Record (SDR):
setAttributes (key, value)
- If
keyis a string, a property with key = value is added to the attributes object in the SDR. - If
keyis an object, all of its properties are added as individual properties in the attributes object in the SDR. In this case,valueis ignored.
Example
// set first key value pair
setAttributes('key1', 'Success')
// add a second one using variables in the application
var varKeyName = "key3"
var varKeyValue = "value3"
setAttributes( varKeyName, varKeyValue)
// lets add an object which will overwrite "key1" and add "key2"
var myObject = { "key1" : "value1", "key2" : "value2" }
setAttributes( myObject )
// All these statements will finally generate this data:
attributesList {
"key1" : "value1",
"key2" : "value2",
"key3" : "value3"
}
Usage and limitations
You can use this function in all phases of Default and Digital applications, in both Self Service and Assisted Service. However, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Do not log Personally Identifiable Information (PII).
- Do not log secure variables.
- Keep the data size less than 25Kb.
isDataTableValueValid
You can use this function to determine if a value returned from a data table query is valid. For example, you might use the following function in an Assign block:
isDataTableValueValid(value, datatype)
This function has two arguments:
- value is a single value returned from a data table query
- datatype is the data type of the data table column, such as 'string', 'boolean', 'integer', 'announcement', or 'numeric' (this argument is optional)
If the data table value is valid, the script returns true. Here is a list of values that this function can return:
isDataTableValueValid(varStr, 'string')on a valid (or empty) string returnstrue. Anything else returnsfalse.isDataTableValueValid(varNum, 'numeric')on a valid number or0returnstrue. Anything else returnsfalse.isDataTableValueValid(varNum, 'integer')on a valid integer or0returnstrue. Anything else returnsfalse.isDataTableValueValid(varBool, 'boolean')ontrueorfalsereturnstrue. Anything else returnsfalse.isDataTableValueValid(varAudio, 'announcement')on a valid (or null) announcement returnstrue. Anything else returnsfalse.