High availability and disaster recovery
Find out how this service provides disaster recovery in the event the service goes down.
| Service | High Availability | Disaster Recovery | Where can you host this service? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Workspace Web Edition | N = N (N+1) | Active-spare | Primary or secondary unit |
See High Availability information for all services: High availability and disaster recovery
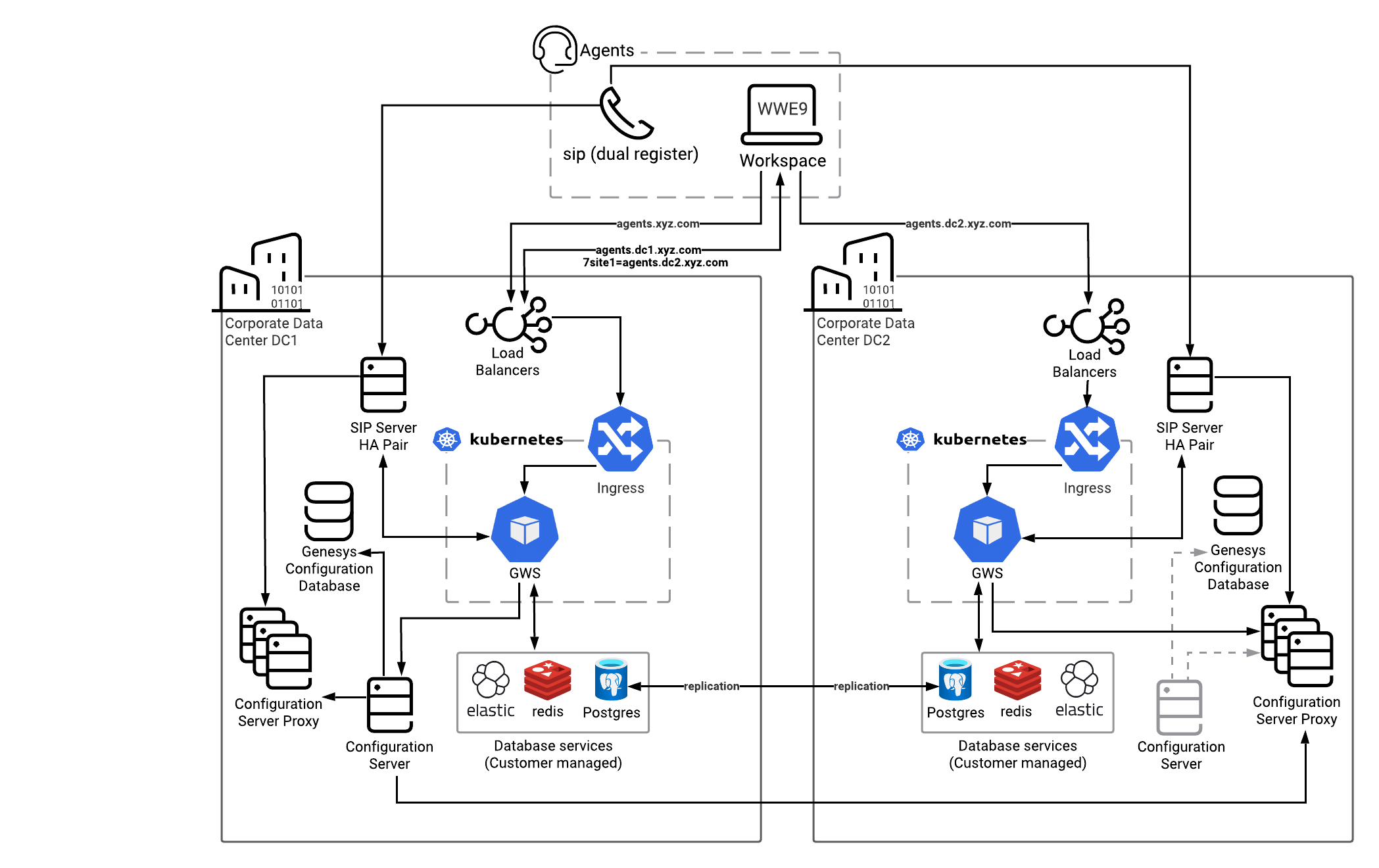
To support High Availability and Disaster Recovery, Workspace Web Edition should be deployed as part of Genesys Web Services in multiple regions.
To maintain business continuity without requiring user manual switching to the backup region, the Workspace Web Edition application (browser-side) automatically fails over to the backup region when it detects a loss of connectivity to the primary region. The application notifies the agent (end user) of the failover operation in progress and might prompt for re-authentication.
Refer to the Architecture topic for information about HLA architecture.
Smart Failover for Workspace Users[ | edit source]
Smart failover support for Workspace users is provided by Genesys Web Services and Applications (GWS).
- SIP phone dual-registers to both data centers.
- SIP HA handles SIP Server failover.
- Various DNs are provisioned in both SIP Servers, so that agents can operate in either SIP Server deployment.
- An agent's browser is set up with a link to the Workspace application. For Smart Failover, DNS resolution is used to return the URL to the local data center's GWS/Workspace app with the address of the backup site specified as the URL parameter.
- CometD connection (through HTTPS) is maintained with the Workspace client.
Workspace Agent Site Selection[ | edit source]
Workspace uses DNS to select and distribute Workspace agents across sites and load balance between nodes.
- The browser uses DNS to resolve the common URL address to the local site. The link to the backup site should also be included in the name resolution:
https://agents.xyz.com
https://agents.dc1.xyz.com?site-1=agents.dc2.xyz.com
- The browser fetches the Workspace application from the data center specified in the DNS (DC1).
- Session stickiness persists the link from the browser app to the GWS instance handling the agent's desktop.
If there is an issue with the current site, Workspace senses this (due to the loss of the CometD connection) and reconnects to the DR site URL specified in the parameter (example, ?site-1=agents.dc2.xyz.com).
DNS configuration is an important element of this solution and depends on your load balancer/proxy. It needs to support name resolution to the local site, addition of the site-X URL parameter, and sticky sessions.
Configuration Server[ | edit source]
Configuration Server Proxies are deployed in both data centers to handle requests for configuration information. One data center has a live Configuration Server for making updates. A cold standby pair exists within the other data center.
During a data center failure, the Configuration Server Proxies in the remaining data center handle requests. Configuration updates are not possible. If needed, the cold standby Configuration Server can be turned on in the remaining data center, assuming that configuration database replication is enabled between sites. If the cold standby Configuration Server is turned on, the Configuration Server Proxies need to re-establish a connection with the new operational Configuration Server. Expect performance impacts from switching over.
Failover Scenarios[ | edit source]
Voice Channel[ | edit source]
If the SIP phone loses connection to SIP Servers in one data center, it re-connects to SIP Servers in the other data center, based on SIP/dual registration protocol. Existing voice calls might be lost.
GWS monitors the connection to the SIP Server session. The connection drops when the SIP Server goes down. GWS notifies an application in the agent's browser about the Voice channel unavailability with the ServiceStateChanged UNAVAILABLE event.
Workspace[ | edit source]
Workspace triggers a disaster recovery failover to another site based on the following triggers:
- DN unregistration (DNStateChanged Inactive event received)
- Voice channel unavailability (ServiceStateChanged UNAVAILABLE event received)
- CometD real-time channel loss
- Workspace initialization issues at login
- Registration failure for Softphone
- Registration failure for WebRTC
The Workspace application needs to authenticate in order to log in to the backup site. The single sign-on (SSO) integration automatically logs in to the backup site without requiring the agent to enter the password.
Data Center[ | edit source]
If the entire data center fails, both the voice channel and the Workspace application fail. This impacts both CometD connections to the Workspace client, forcing it to reconnect to the backup site. The SIP endpoint also switches over to the other site.