Difference between revisions of "Docker/Current/Troubleshooting/Running Containers"
(Published) |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|Section={{Section | |Section={{Section | ||
|sectionHeading=Running Containers | |sectionHeading=Running Containers | ||
| − | | | + | |Standalone=No |
| − | | | + | |ComingSoon=No |
| + | |Status=No | ||
| + | |alignment=Vertical | ||
| + | |structuredtext=Containers are running instances of an Image. To run containers, follow these steps: | ||
# Create a container from the base image for the latest version of the Ubuntu that is available. | # Create a container from the base image for the latest version of the Ubuntu that is available. | ||
#: {{NoteFormat| | #: {{NoteFormat| | ||
| Line 19: | Line 22: | ||
}}{{Section | }}{{Section | ||
|sectionHeading=Lifecycle | |sectionHeading=Lifecycle | ||
| − | | | + | |Standalone=No |
| − | | | + | |ComingSoon=No |
| + | |Status=No | ||
| + | |alignment=Vertical | ||
| + | |structuredtext=The following commands illustrate the Docker Lifecycle: | ||
* <code>docker create</code> creates a container but does not start the container. | * <code>docker create</code> creates a container but does not start the container. | ||
* <code>docker rename</code> allows the container to be renamed. | * <code>docker rename</code> allows the container to be renamed. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 46: | ||
}}{{Section | }}{{Section | ||
|sectionHeading=Starting and Stopping a Container | |sectionHeading=Starting and Stopping a Container | ||
| − | | | + | |Standalone=No |
| − | | | + | |ComingSoon=No |
| + | |Status=No | ||
| + | |alignment=Vertical | ||
| + | |structuredtext=Commands to start and stop a container: | ||
* <code>docker start</code> starts a container so it is running. | * <code>docker start</code> starts a container so it is running. | ||
* <code>docker stop</code> stops a running container. | * <code>docker stop</code> stops a running container. | ||
Revision as of 13:36, January 17, 2020
Instructions to run the Docker containers.
Running Containers
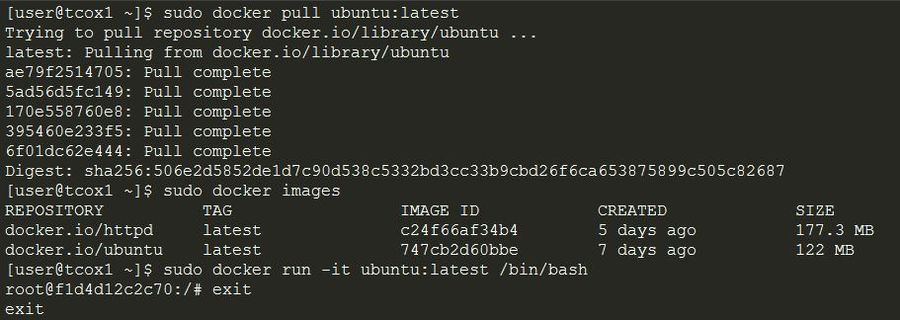
Containers are running instances of an Image. To run containers, follow these steps:
- Create a container from the base image for the latest version of the Ubuntu that is available.
- Important
- If you do not have an Ubuntu base image installed locally, extract the latest one for your local repository.
- You must start the container in interactive mode attached to the current terminal and running the bash shell.
- After running, make sure you shut down the container by running 'exit'.
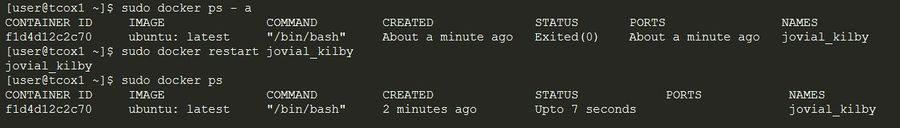
Lifecycle
The following commands illustrate the Docker Lifecycle:
docker createcreates a container but does not start the container.docker renameallows the container to be renamed.docker runcreates and starts a container in a single operation.docker rmdeletes a container.docker updateupdates a container's resource limits.
Usually, when you run a container without options, it will start and stop immediately. If you want the container to keep running, you can use the command, docker run -td container_ID. This command uses the option-t to allocate a pseudo-TTY session and option-d to detach the container automatically (you can run container in background and print the container ID).
To have a transient container, use the command docker run –rm. This command will remove the container after it stops.
To map a directory on the host to a docker container, use the command docker run -v $HOSTDIR:$DOCKERDIR<.
To remove the volumes associated with the container, the deletion of the container must include the option-vswitch like in docker rm -v.
There is also a logging driver available for individual containers in docker 1.10. To run docker with a custom log driver (that is syslog), use the command docker run --log-driver=syslog.
docker run --name yourname docker_image is a useful command because when you specify --name inside the run command, you can start and stop a container by calling it with the name that you specified when you created it.
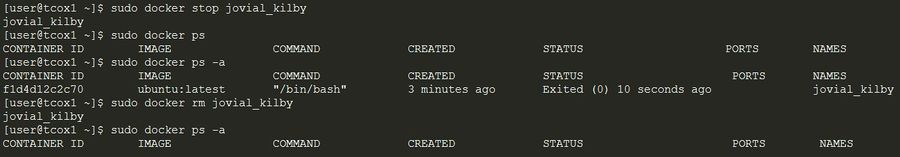
Starting and Stopping a Container
Commands to start and stop a container:
docker startstarts a container so it is running.docker stopstops a running container.docker restartstops and starts a container.docker pausepauses a running container, "freezing" it in place.docker unpauseunpauses a running container.docker waitblocks until running container stops.docker killsends a SIGKILL signal to a running container.docker attachconnects to a running container.
To integrate a container with a host process manager, start the daemon with the commands -r=false and then use docker start -a.